Are AI Detectors better at detecting Human Created Images or AI-Generated Ones?
The rise of Artificial Intelligence is a subject of debate around the world, with many people concerned that AI will overtake creative industries and compound the disruption in every industry, whilst others find it a perfect solution to the difficulties of working life.
As AI tools become more accessible to everyday people, they are now widely used for creating artwork and images. This has led to the ability to create images at volume with higher consistency and a higher rate. But it has also led to ramifications of inaccuracies, bias and a phenomenon called ‘deepfakes’ which can be used to spread mass misinformation.
To counteract this and to discern AI from non-AI, tools that can detect AI were created, using processes that spot patterns common in AI by gathering data and analyzing content continuously. This is done from input of AI examples and human examples to teach the detector the difference – but how accurate are they?
KnownHost created a new study to look at how AI Detectors detect both images created by humans and images created by AI. For images created by humans, stock images were used to ensure the images were valid as not AI, whilst the AI images were generated from four different AI Image generators. These were then compared to discover which is easier to detect.
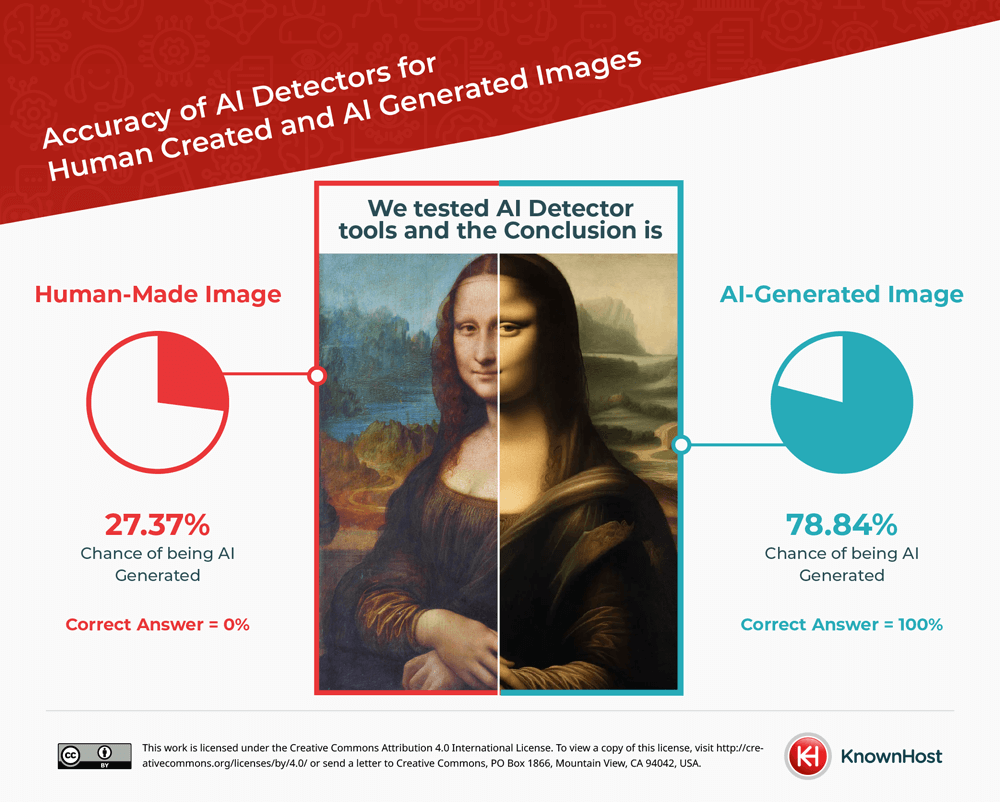
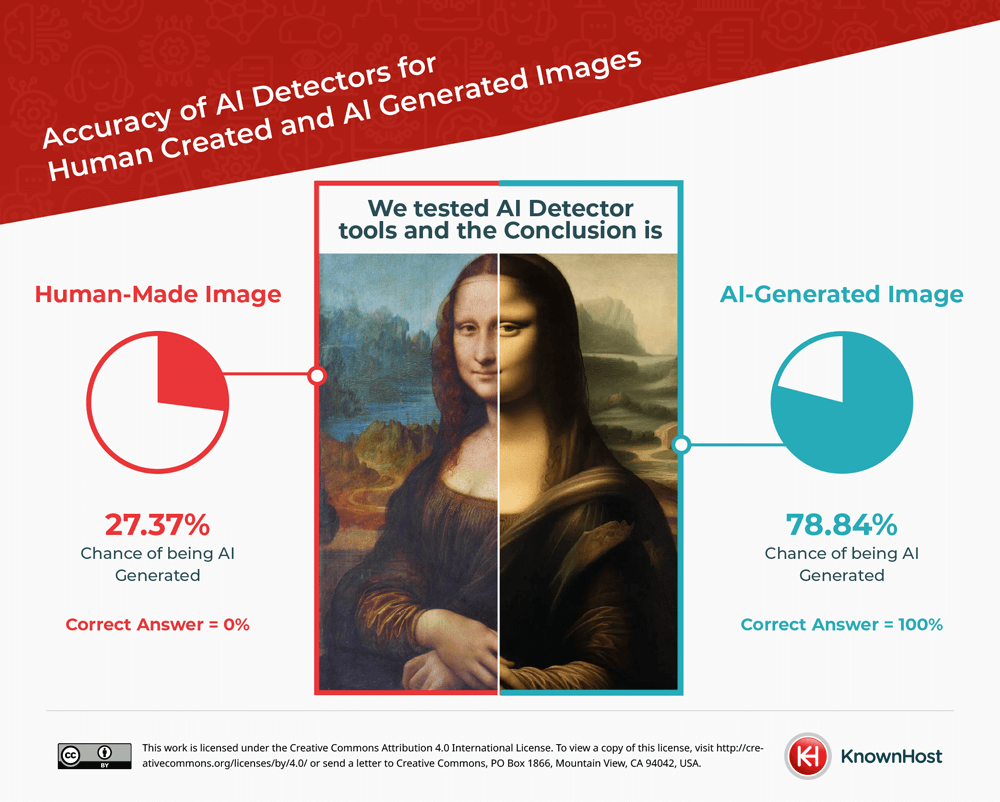
AI Detectors Overall Accuracy
AI Detectors on AI Images
When the AI detectors were analyzing the AI-generated images, they were able to detect an average AI likelihood of 78.84% across all the two hundred AI images that were inputted. This represents a slightly lower detection rate than expected.
AI Detectors on Human Created Images
For human-created images, the detectors found an AI likelihood of 27.37% across the fifty stock images that were processed. Similarly, this is a higher likelihood than expected with human-created images.
AI Detectors Accuracy per Section
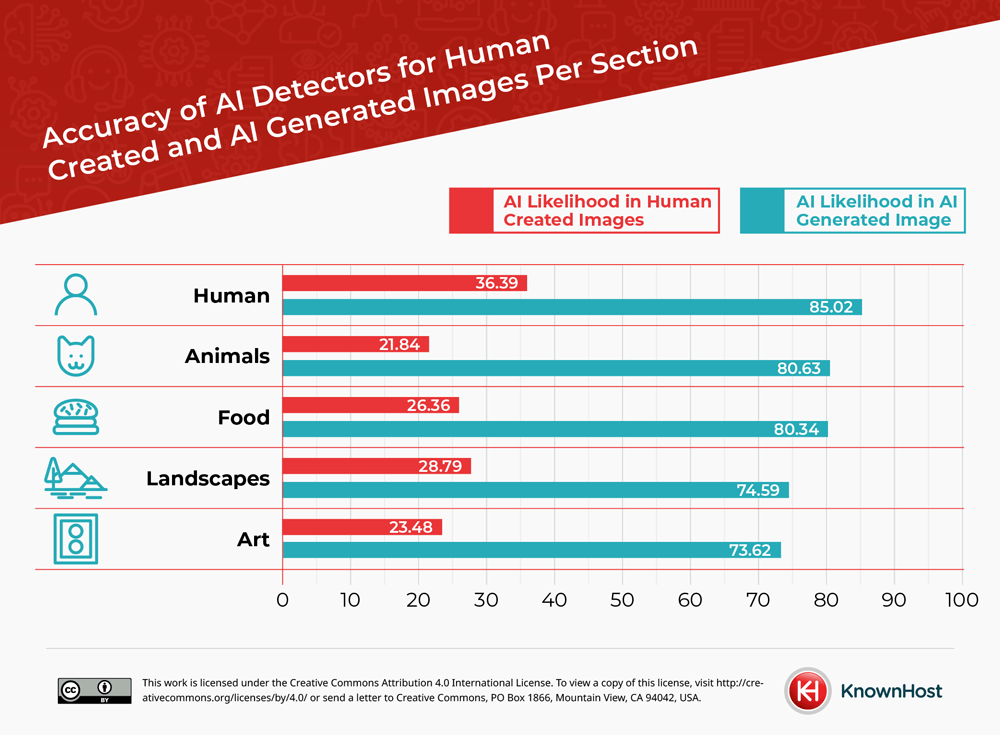
When looking at the different sections that were used to establish the types of images that were generated, it proved an interesting insight into the accuracy of certain types of images and how accurately they were detected as a subsidiary test. Each section had 10 images created by each AI-generator and ten human-created images which were then tested for AI likelihood.
These were the results:
Human
AI-Generated images of humans had the highest likelihood of being detected as AI with an 85.02% likelihood of AI, which suggests the processing of human detail information for detection is lower than other image faculties.
However, AI detectors had difficulty identifying human-created images as real. The AI detectors incorrectly found that real images of humans had an AI likelihood at 36.39%.
Animals
The section of Animals had the second highest AI likelihood with its AI-generated images with an AI likelihood of 80.63%, but the lowest AI likelihood with its human-created images at 21.84%.
Food
Real images of food had the third highest AI likelihood, revealing that AI detectors have trouble correctly identifying whether images are AI-generated or not. AI detectors found that human-created images had a 26.36% chance of being AI-generated. However, AI detectors were more successful correctly identifying AI-generated images of food. AI-generated images of food had an average of 80.34% AI likelihood.
Landscapes
The fourth most accurate category was landscapes. AI detectors found that AI-generated images of landscapes have a 74.59% likelihood of being AI generated. The study revealed that AI detectors have trouble identifying human-created images. AI detectors incorrectly found that human-created images have an average of 28.79% AI likelihood.
Art
Alternatively, the AI Detectors had the lowest accuracy with identifying AI-generated art. AI generators were told to recreate either famous artworks, like the Mona Lisa, or art from a certain artistic movement like neoclassicism. AI-generated images were only flagged with 73.62 percent likelihood of being AI-generated.
Which AI Generators Create the Most Detectable Images?
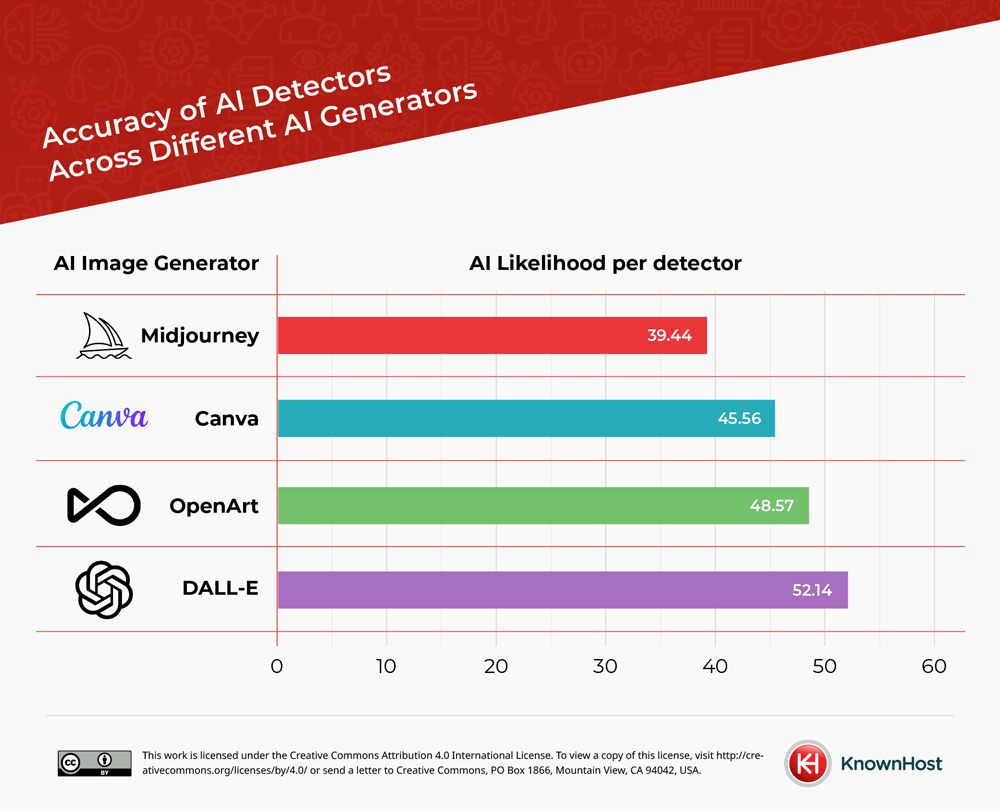
The four generators used in this study are Midjourney, Canva, OpenArt and DALL-E. These created images according to inputted prompts and generated images across the sections.
DALL-E was the most easily detected AI image generator with an average AI likelihood of 52.14% of its generated images. This is a tool developed by Open AI, which was first released in 2021, but it’s latest model, DALL-E 3 was used in this study.
Midjourney was the least likely to be detected with its images having an AI likelihood of 39.44% being detected as AI. Midjourney was created in 2022 and uses Discord bot commands to create its images. Canva’s AI-generative tools were released in 2022 as was OpenArt. Due to these three tools being released later, this could suggest that over time, the AI images will be more likely to be detected as this is the main difference between the generators.
Conclusion
To summarize, the most inaccurate detection was on human-created images of humans and the most accurate detection was on AI-generated images of human, which reveals how the detectors are likely to think any image of a human being could be AI-generated. The detectors were correct overall in their decision, but the accuracy level was lower. This shows that AI detection is still far from where it should be, to ensure safety in case of the spreading of deepfake images and using real people’s likeness in harmful ways.
The slight inaccuracy shows that detectors of AI are not completely dependable tools to ensure that AI images are distinguishable from non-AI images, therefore improvements to refine the accuracy are needed so that AI remains useful rather than hindered by the potential dangers they are associated with.
Methodology
For the methodology, we generated images across five sections with 10 images per theme – Art, Animals, Landscapes, Human (beings) and Food – using four different AI image generators, alongside a human-created image from Adobe Stock. These images were then tested across three detectors to test if accuracy of each detector.


